What is Edge Computing?
Edge computing is a distributed computing model in which computing takes place near the physical location where data is being collected and analyzed, rather than on a centralized server or in the cloud. This new infrastructure involves sensors to collect data and edge servers to securely process data in real-time on site, while also connecting other devices, like laptops and smartphones, to the network.
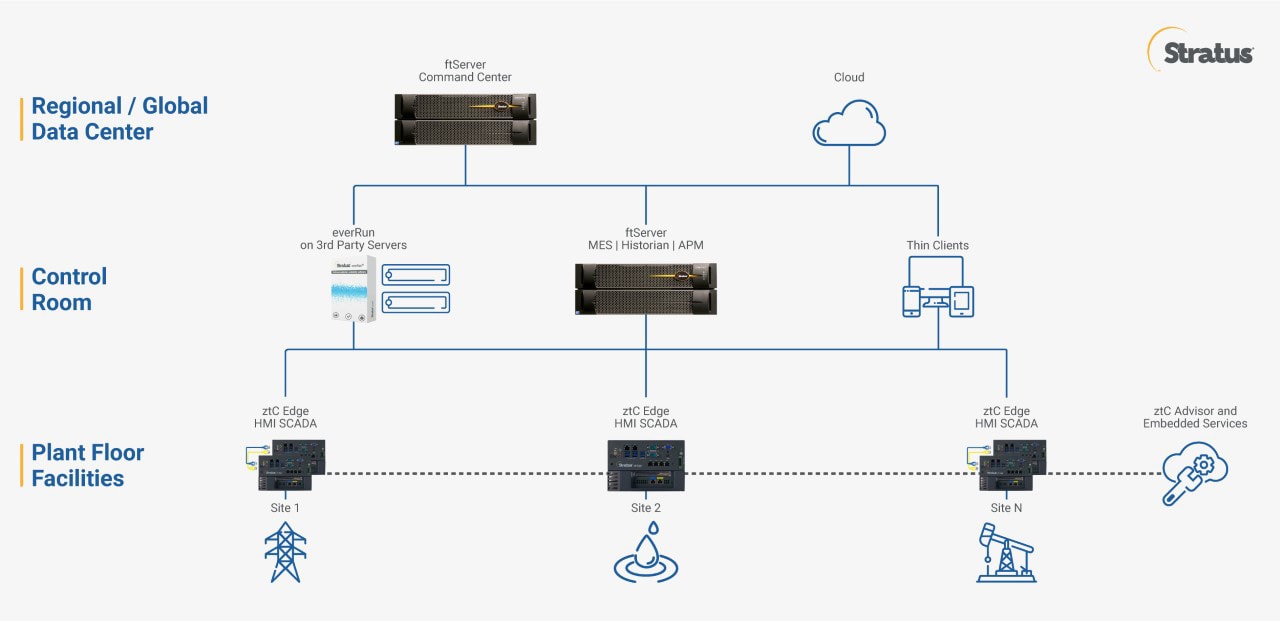
Edge Computing Ecosystem

By 2025, 175 zettabytes (or 175 trillion gigabytes) of data will be generated around the globe. Edge devices will create more than 90 zettabytes of that data.
-IDC Data Age 2025 report The Digitization of the World: From Edge to Core
Explore Edge Computing
Why is Edge Computing Important?
Edge computing is important because it creates new and improved ways for industrial and enterprise-level businesses to maximize operational efficiency, improve performance and safety, automate all core business processes, and ensure “always on” availability. It is a leading method to achieve the digital transformation of how you do business.
Increasing computing power at the edge is the foundation needed to establish autonomous systems, enabling companies to increase efficiency and productivity while enabling personnel to focus on higher value activities within the operation.

Benefits of Edge Computing
One of the top benefits of implementing edge computing is the ability to collect and analyze data where it is collected, catching and correcting problems that might not be identified as quickly if the data were to be sent to a central server or cloud for processing and analysis. Keeping data on site also reduces the security risk associated with porting data, which can be important in financial organizations, for example. It also reduces bandwidth costs by processing some data on site, rather than sending all data to a cloud or central server.

Challenges in Edge Computing
Successful edge computing requires a thoughtful architecture and implementation , which can be a challenge without the right expertise. Having multitudes of sites collecting and analyzing data can mean more sites that need to be configured and monitored, adding complexity. Having too few can mean critical data is missed. Decentralized locations can also mean fewer technical personnel on site, meaning non-technical operations staff may be called in to troubleshoot. These challenges can be addressed by working with knowledgeable system integrators and using the right edge technology.

Security at the Edge
Because edge computing is distributed, the security risk is different than a centralized environment. The security controls found in private data centers or public clouds, like firewalls or antivirus tools, don’t automatically transfer. Experts recommend a few simple steps, including hardening each host, real-time network monitoring, encrypting data, and adding physical security measures.

The Cloud and the Edge
Does the Edge Replace the Cloud?
Edge computing works hand in hand with the cloud to provide a flexible solution based on the data collection and analysis needs of each organization. For real-time collection and analysis, the edge is ideal for certain workloads. At the same time, the cloud can provide a centralized location for large scale analytics. Together they provide real-time and longer term insights into performance and power initiatives like machine learning and asset performance management.
Hybrid Cloud and the Edge
If you’re already using a hybrid cloud architecture, then you’re familiar with the benefits of partitioning data between public and private clouds. Edge computing can be a great addition to this existing network. There are different configurations, and all work well, depending on your business goals and usage. For example, the edge can take the place of the private cloud, taking the primary computing role, or you can pair the edge with an existing hybrid cloud with both public and private clouds.
Edge Computing Resources

Success Stories From the Edge
This compendium represents a series of Edge Computing case studies and success stories from companies working with Stratus.

Edge Computing 101
This practice guide to Edge Computing discusses Edge Computing in terms meaningful for those actively engaged in defining automation solutions.

Edge Computing For Dummies
Edge Computing for Dummies can get you started on the path to Edge Computing success.
Trusted by Stratus Partners

Edge Computing Solutions
ztC Edge
Stratus’ newest solution, ztC Edge, was specifically designed for the edge. Stratus ztC Edge is a secure, rugged, highly automated computing platform that delivers business-critical industrial applications quickly, reliably, and efficiently, even in decentralized, understaffed locations.

ftServer
Optimized for Edge Computing, Stratus ftServer delivers the performance needed to support your advanced processor and data intensive applications, while also providing the fault tolerance, security and manageability required at the edge of your corporate networks.


